Two distinct filling technologies are available for semi-automatic and fully automatic filling machines: volumetric and vacuum-level filling.
Manually operated filling machines tend only to fill volumetrically.
Volumetric filling machines
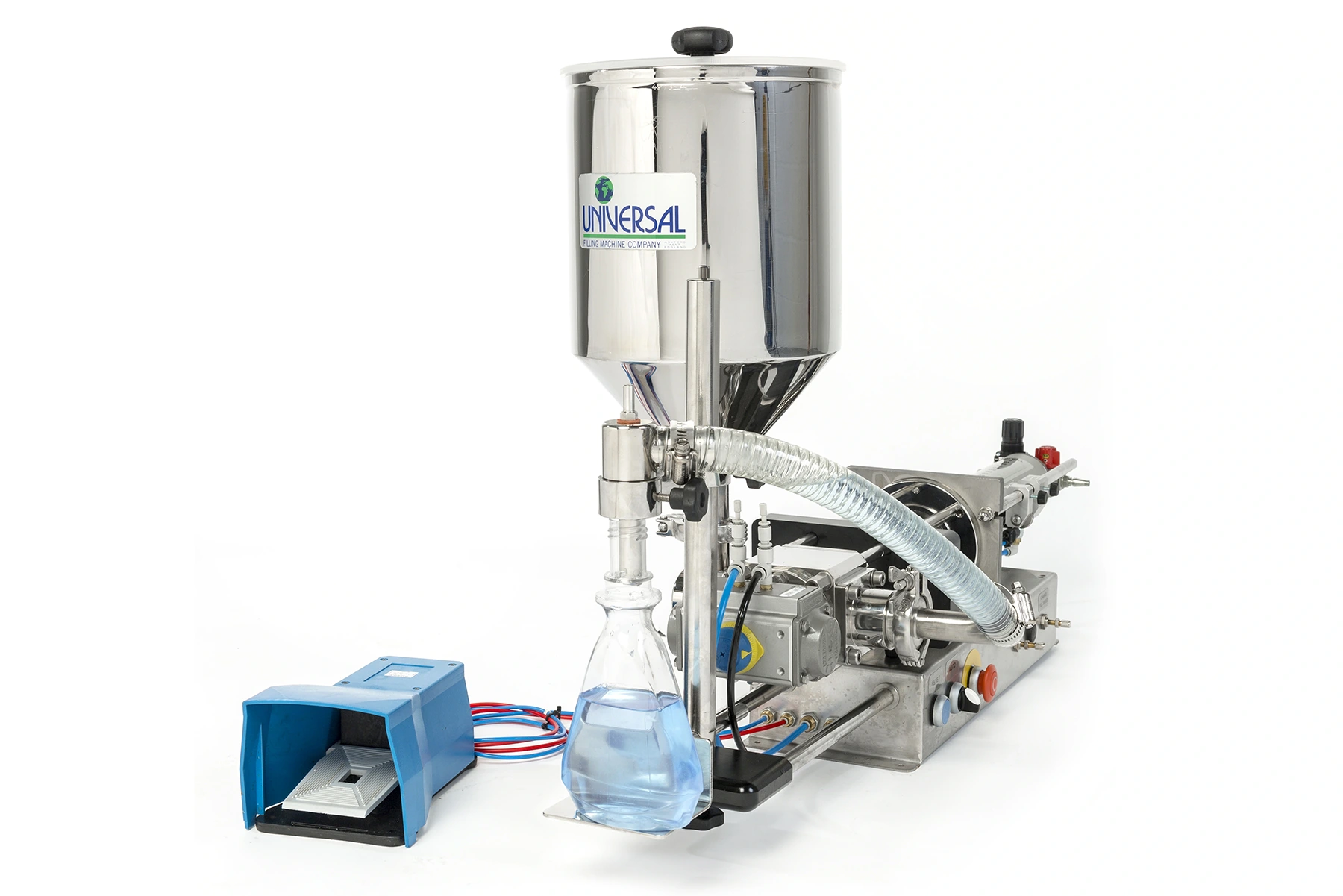
Manual liquid filling machines use a piston within a cylinder to force liquid into the container.
These normally have a pneumatically powered pump mechanism, set to fill containers with the required volume of liquid, fed from either a floor-standing container or a machine-mounted hopper.
Containers are positioned below the filling nozzles and a foot pedal switch to start the filling process.
Volumes between 5ml and 25-litres can be handled by volumetric filling machines and up to 150 containers per minute can be filled, depending on the fill volume, liquid viscosity and level of machine automation.

Vacuum level filling machines
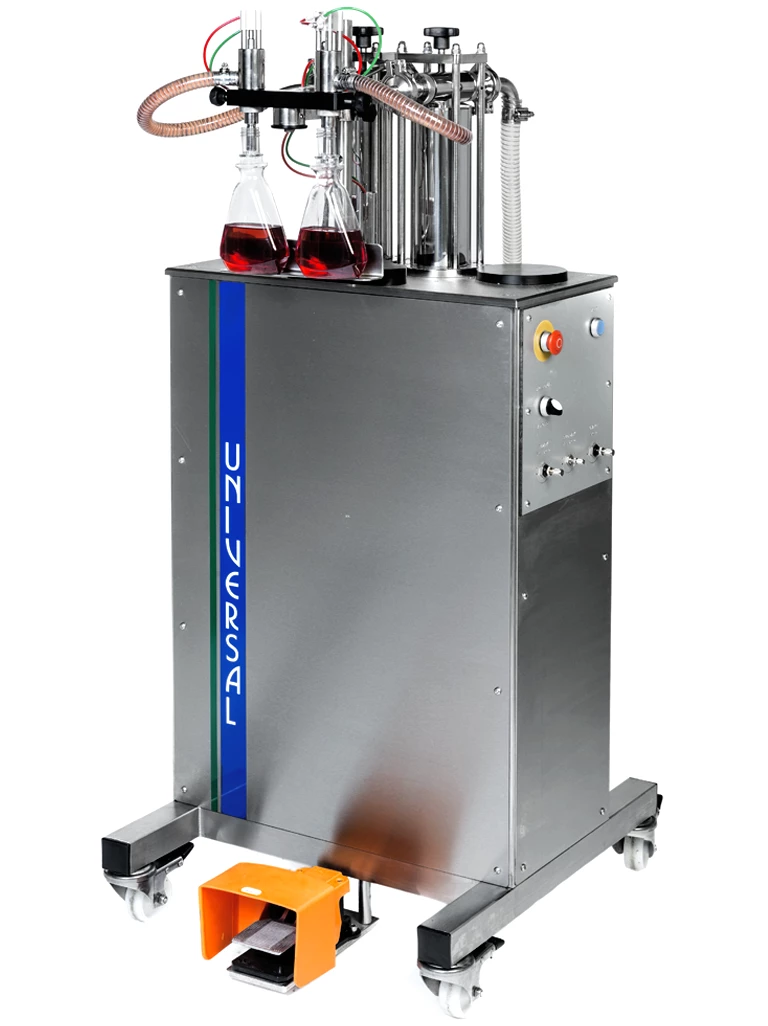
Vacuum level semi-automatic filling machines use the rim at the top of the container to form an airtight seal around the filling nozzle.
This airtight seal creates a vacuum within the bottle which draws free-flowing liquids from a supply tank into the bottle, via specially designed nozzles. These nozzles have a small hole on the side which is connected to a small internal tube.
The height of this hole in relation to the top of the container during filling determines the level of liquid dispensed. The small hole in the nozzle scavenges excess liquid from the filling process and collects it in a receiver for reuse.
Vacuum level filling machines fill containers to the same height each time, rather than dispensing the same volume. This is particularly useful for glass bottles which will be side-by-side on display shelves in shops. Glass bottles vary in capacity quite a lot, yet vacuum-level filling ensures the level each bottle is filled to is the same, giving a consistent appearance from one bottle to the next. Vacuum level filling requires rigid containers which won’t collapse under a vacuum.
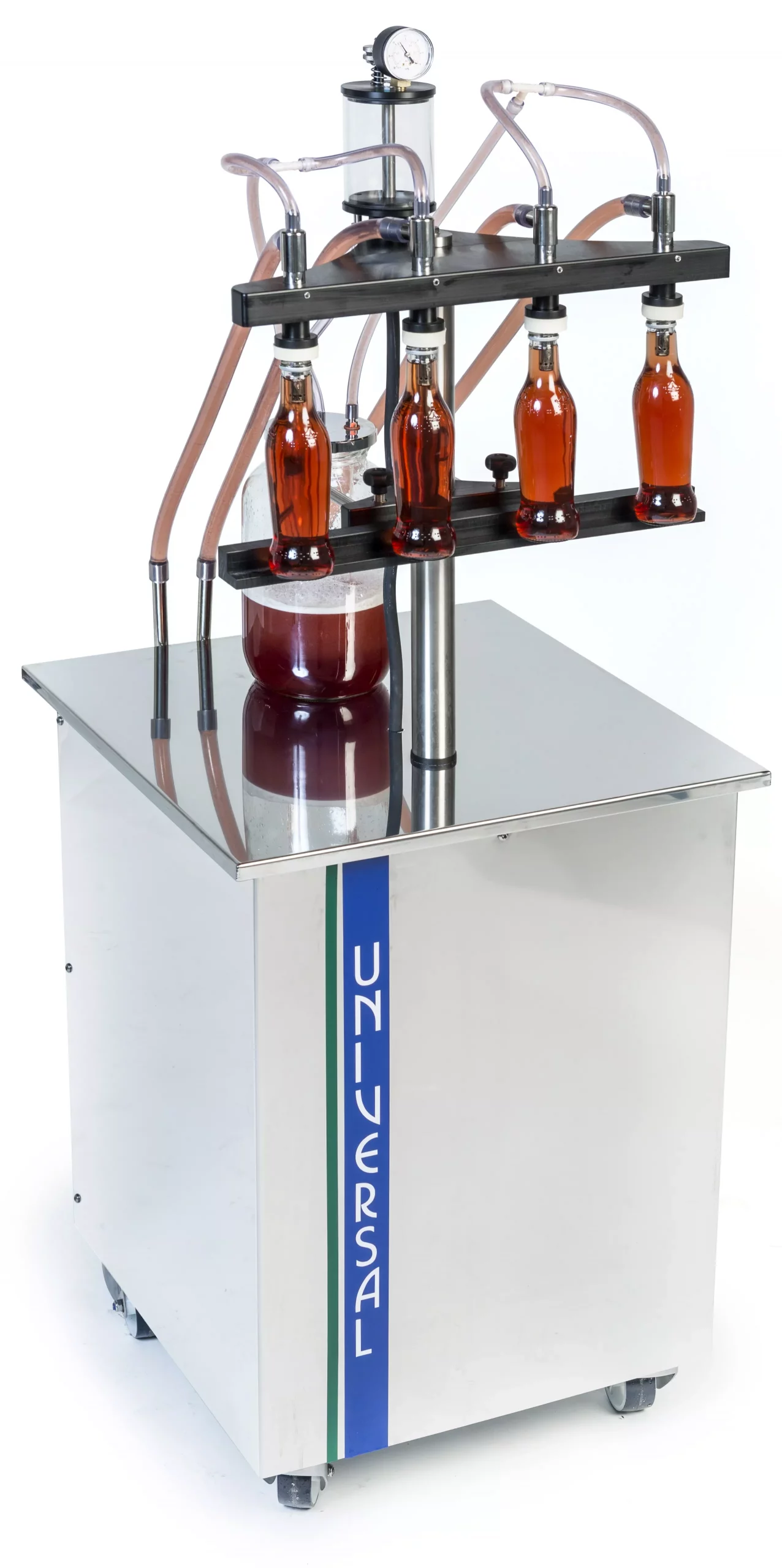

Vacuum-level machines have virtually no moving parts, making them incredibly reliable, and can fill up to 120 bottles per minute depending on the container type, number of filling heads and level of automation.
Bottles are simply positioned with their top in contact with a sealing ring around the nozzle. The container will start to fill as soon as an airtight seal is made and stop when the pre-determined fill height is reached.
Two distinct filling technologies are available for semi-automatic and fully automatic filling machines: volumetric and vacuum-level filling.
Manually operated filling machines tend only to fill volumetrically.
Volumetric filling machines
Manual liquid filling machines use a piston within a cylinder to force liquid into the container.
These normally have a pneumatically powered pump mechanism, set to fill containers with the required volume of liquid, fed from either a floor-standing container or a machine-mounted hopper.
Containers are positioned below the filling nozzles and a foot pedal switch to start the filling process.
Volumes between 5ml and 25-litres can be handled by volumetric filling machines and up to 150 containers per minute can be filled, depending on the fill volume, liquid viscosity and level of machine automation.

Vacuum level filling machines
Vacuum level semi-automatic filling machines use the rim at the top of the container to form an airtight seal around the filling nozzle.

This airtight seal creates a vacuum within the bottle which draws free-flowing liquids from a supply tank into the bottle, via specially designed nozzles. These nozzles have a small hole on the side which is connected to a small internal tube.
The height of this hole in relation to the top of the container during filling determines the level of liquid dispensed. The small hole in the nozzle scavenges excess liquid from the filling process and collects it in a receiver for reuse.
Vacuum level filling machines fill containers to the same height each time, rather than dispensing the same volume. This is particularly useful for glass bottles which will be side-by-side on display shelves in shops. Glass bottles vary in capacity quite a lot, yet vacuum-level filling ensures the level each bottle is filled to is the same, giving a consistent appearance from one bottle to the next. Vacuum level filling requires rigid containers which won’t collapse under a vacuum.
Vacuum-level machines have virtually no moving parts, making them incredibly reliable, and can fill up to 120 bottles per minute depending on the container type, number of filling heads and level of automation.
Bottles are simply positioned with their top in contact with a sealing ring around the nozzle. The container will start to fill as soon as an airtight seal is made and stop when the pre-determined fill height is reached.
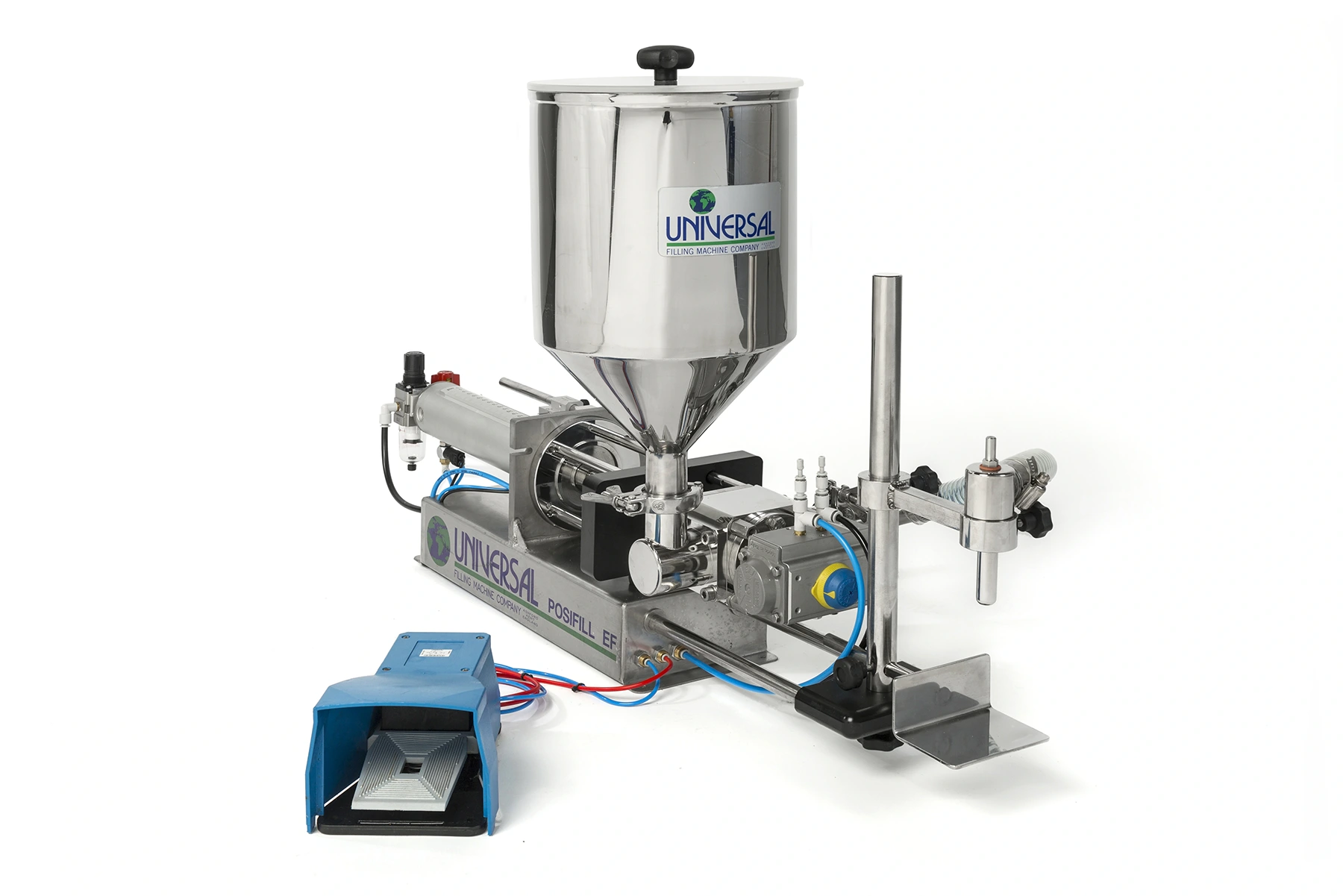
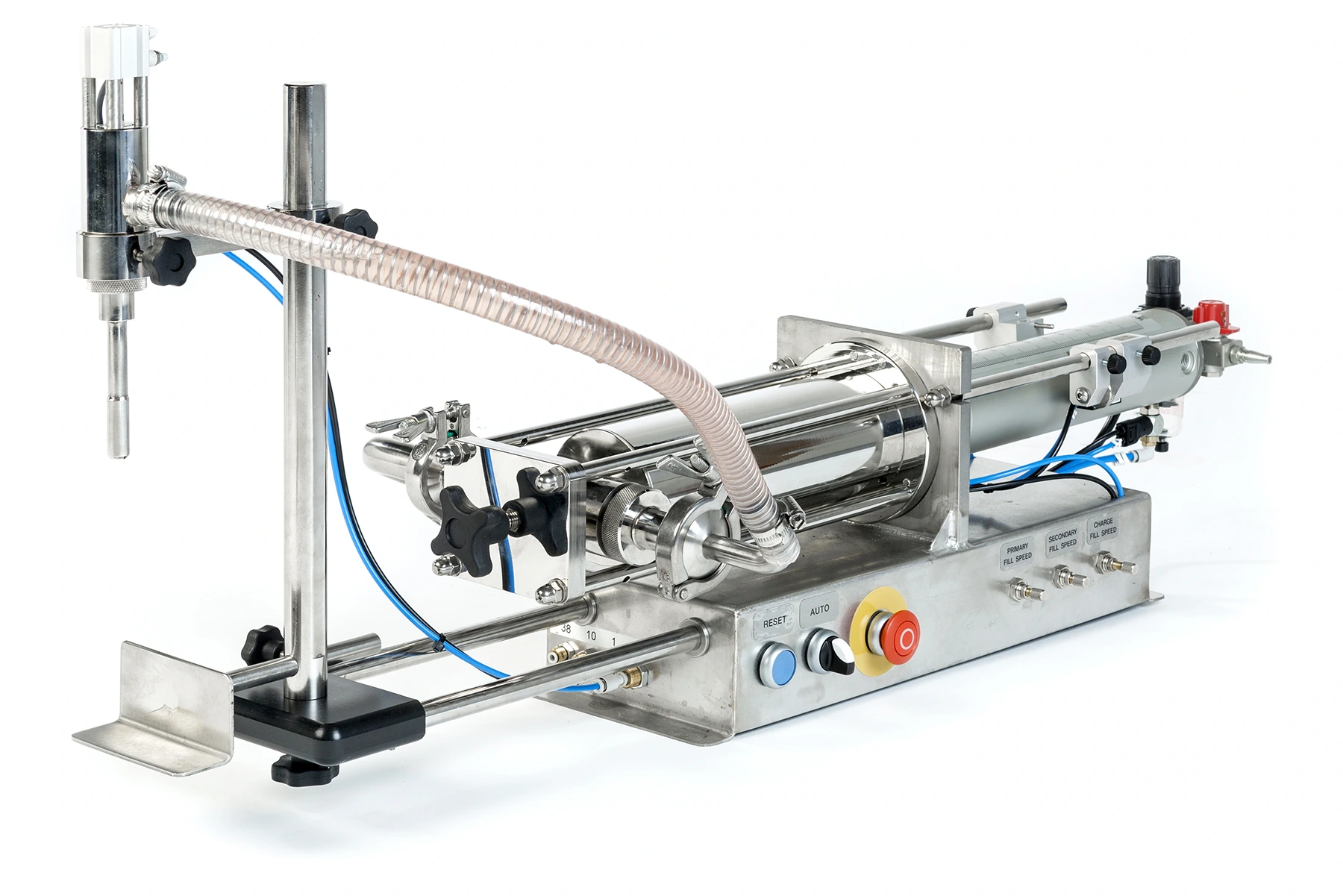
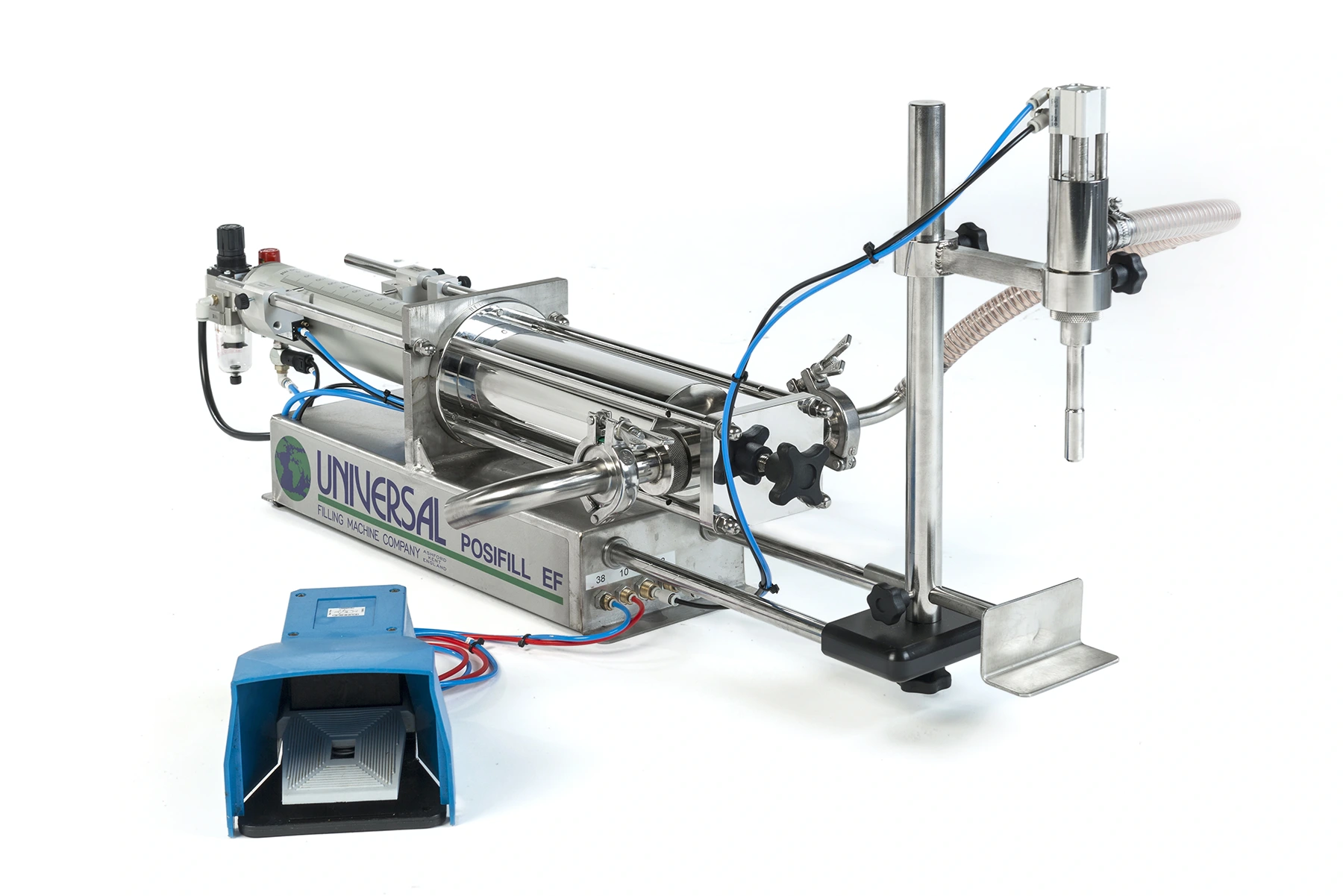
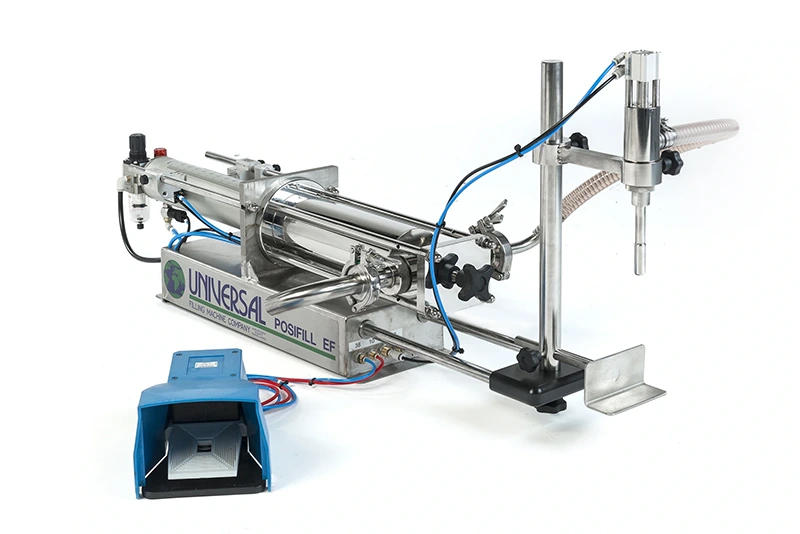
The Posifill EF piston filler is a semi-automatic volumetric liquid filling machine manufactured by Universal Filling Machine Company, in the UK.
It is designed to accurately fill containers with a wide range of liquid products, including thin liquids, viscous products, and products with particulates.
The Posifill EF uses a piston and cylinder system to draw and dispense liquid, allowing for accurate and repeatable fills. It is a semi-automatic machine, which means that it can fill a large number of containers quickly and efficiently.
It is available with either a 5ml – 1,300ml or 200ml – 2,500ml filling range and is capable of filling up to 30 bottles per minute; depending on operator dexterity.
The Posifill EF features a stainless steel frame and food and pharmaceutical grade 316 stainless steel contact parts, making it durable and easy to clean. It also feature simple controls, which allows the operator to easily adjust fill volumes and speeds.
A wide variety of options are available for the Posifill EF to optimise it for any filling application, from pneumatic shut-off nozzles to rotary metering valves, secondary fill speed controls and multi-dose counters.
Overall, the Posifill EF piston filler is a high-quality, reliable and efficient liquid filling machine that can help improve the productivity and accuracy of liquid filling operations in industries such as food and beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.